Ovid
Join the John Miller Burnam Classics Library 5:30-7:30 p.m., Thursday, March 29 in 417 Blegen Library for “An Evening with Ovid,” an event celebrating the life and work of the Roman poet. We will raise a glass in his honor in connection with his birthday and the 2,000-year anniversary of his death.
The evening will begin with welcoming remarks by Rebecka Lindau, head of the Classics Library. Bridget Langley, visiting assistant professor in the College of Arts and Sciences’ Department of Classics, will give a brief presentation of Ovid’s life and work. Colin Shelton, adjunct professor in Classics, will follow with a reading of two of Ovid’s Metamorphoses in Latin and in translation by modern English poet Ted Hughes. Jenny Doctor, head of the Albino Gorno Memorial Music Library, will introduce a musical performance by modern English composer Benjamin Britten, “Six Metamorphoses after Ovid,” featuring College-Conservatory of Music oboist Yo Shionoya.

Ovid’s Metamorphoses
The evening will conclude with refreshments Ovid and his contemporaries would have enjoyed. The event will be presided over by Emperor Augustus himself in the form of a copy of the original marble head discovered at Troy during an excavation led by UC’s Classics Department. Additionally, the library will feature a book exhibition with works of Ovid, including rare editions of the Metamorphoses.
The event is free and open to all. RSVP to Cade Stevens at stevencd@ucmail.uc.edu or 513-556-1314 by Friday, March 23.
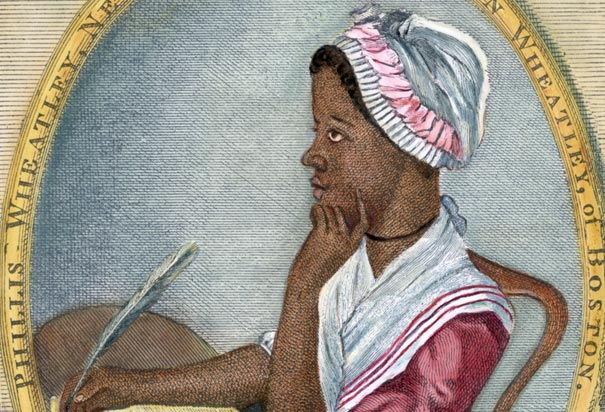




 In celebration of Black History Month, UC Libraries is holding an event featuring poetry and poet Phillis Wheatley, the first published African-American poet.
In celebration of Black History Month, UC Libraries is holding an event featuring poetry and poet Phillis Wheatley, the first published African-American poet. The University of Cincinnati Libraries and IT@UC announce the third annual UC DATA Day. Scheduled for 8:30 a.m.-4:15 p.m., Tuesday, March 6 in Nippert Stadium West Pavilion on UC’s Main Campus (see
The University of Cincinnati Libraries and IT@UC announce the third annual UC DATA Day. Scheduled for 8:30 a.m.-4:15 p.m., Tuesday, March 6 in Nippert Stadium West Pavilion on UC’s Main Campus (see 


