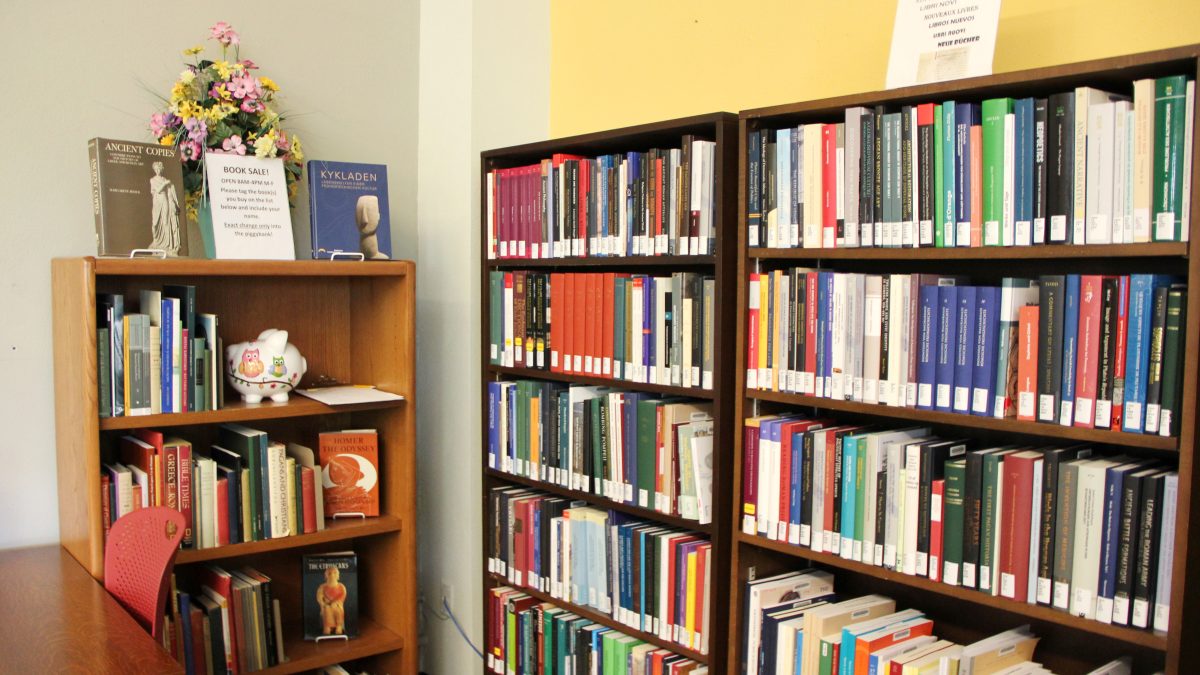
I don’t know about you, but every time I walk into our Classics Library, I feel a little like Indiana Jones. As I admire the priceless treasures housed there, I can’t shake the sneaking suspicion that at any moment, a huge boulder is going to appear and start chasing me, threatening to run me over. After all, being surrounded by the collected wisdom of the ancient world creates an atmosphere like none other, teeming with whispers of long-ago adventures and still-uncovered secrets.
The University of Cincinnati’s (UC) John Miller Burnam Classics Library is undoubtedly one of a kind. From its inception to its current practices, the library holds a special place in the heart of our Classics Department, libraries, and wider scholarly community, serving distinguished international faculty, graduate and undergraduate students, and many visiting scholars. It is the definition of a destination library, serving over 75,000 patrons from around the world per year, who flock to Cincinnati to browse and study its unparalleled resources.
Classics alumna, Lindsay Taylor, agrees the Classics Library is a very special place. “It probably saved me thousands of dollars as a student to have all these materials at my disposal while doing high-level research. Classics was truly the most magical and scholarly place possible to get an undergraduate degree, and the older I get, the more I realize how valuable the education I received there is. The program is just steeped in evidence and primary source evaluation and scholarly communication surrounding this evaluation, the library is at the core of that effort.”