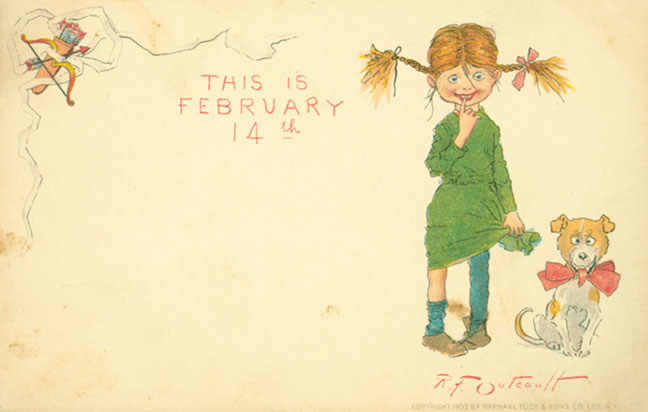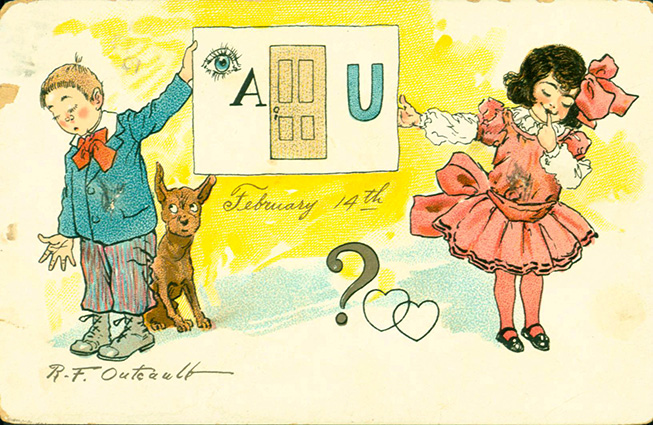By: Kevin Grace
 The children are either drawn as freckle-faced street urchins or as the clean-smocked offspring of the hoity-toity. The animals – a parrot, typically dogs – look on quizzically or crack wise. And the occasion being Valentine’s Day, the messages are about the lovelorn and the hopeful. These are the early 20th century postcards drawn by Richard Felton Outcault, a pioneer of the modern newspaper comic strip who gave America such literary figures as Buster Brown and The Yellow Kid. And advertising being
The children are either drawn as freckle-faced street urchins or as the clean-smocked offspring of the hoity-toity. The animals – a parrot, typically dogs – look on quizzically or crack wise. And the occasion being Valentine’s Day, the messages are about the lovelorn and the hopeful. These are the early 20th century postcards drawn by Richard Felton Outcault, a pioneer of the modern newspaper comic strip who gave America such literary figures as Buster Brown and The Yellow Kid. And advertising being  what it was (and is), Buster and the Kid gave us books, shoes, coin banks, calendars, clocks, pencils, puzzles, and all manner of geegaws, selling the country on the all-American pastime of buying stuff.
what it was (and is), Buster and the Kid gave us books, shoes, coin banks, calendars, clocks, pencils, puzzles, and all manner of geegaws, selling the country on the all-American pastime of buying stuff.
But the postcards deviated from the overall merchandising a bit, although Outcault’s newspaper employers and their agents certainly generated a lot of them. The holiday cards were something a little different, a reflection of the artist’s own attitudes to his comic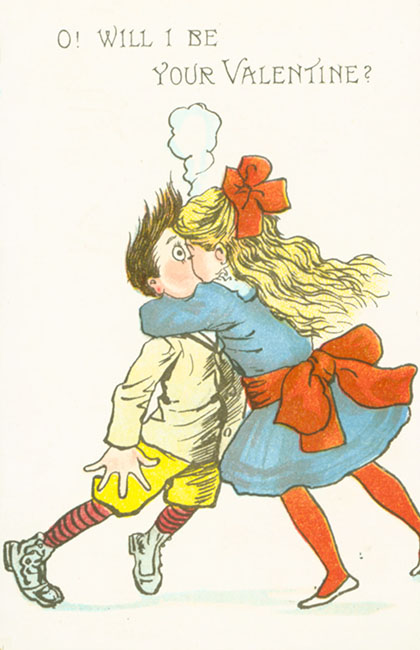  creations. R.F. Outcault was born in 1863, hailing from Lancaster, Ohio. He came to Cincinnati in 1878 to attend the McMicken School of Design – which is now the Cincinnati Art Academy, though the University of Cincinnati certainly traces part of its heritage as well to the McMicken school, so in effect Outcault is a UC alumnus. He graduated in 1881 and began his employment as a painter of bucolic scenes in the massive safes constructed by the Hall Safe and Lock Company. Growing in local reputation, Outcault managed to land a job with the 1888 centennial industrial exposition in Cincinnati, one of the many local product fairs held in the 19th century, and which were begun as an outlet of the Ohio Mechanics Institute, founded in
creations. R.F. Outcault was born in 1863, hailing from Lancaster, Ohio. He came to Cincinnati in 1878 to attend the McMicken School of Design – which is now the Cincinnati Art Academy, though the University of Cincinnati certainly traces part of its heritage as well to the McMicken school, so in effect Outcault is a UC alumnus. He graduated in 1881 and began his employment as a painter of bucolic scenes in the massive safes constructed by the Hall Safe and Lock Company. Growing in local reputation, Outcault managed to land a job with the 1888 centennial industrial exposition in Cincinnati, one of the many local product fairs held in the 19th century, and which were begun as an outlet of the Ohio Mechanics Institute, founded in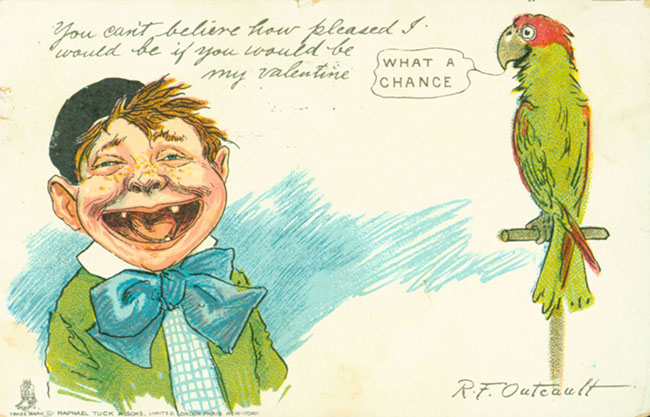  1828 and now part of the University of Cincinnati’s College of Engineering and Applied Science. At the exposition he painted scenes for Thomas Edison’s electric light displays, parlaying that into a career on the east coast with trade magazines. Incidentally, while Edison was a telegraph operator in 1860s Cincinnati, he frequented the OMI library for his reading pleasure.
1828 and now part of the University of Cincinnati’s College of Engineering and Applied Science. At the exposition he painted scenes for Thomas Edison’s electric light displays, parlaying that into a career on the east coast with trade magazines. Incidentally, while Edison was a telegraph operator in 1860s Cincinnati, he frequented the OMI library for his reading pleasure.
By 1894, Outcault was drawing cartoons for newspapers and magazines, particularly the New 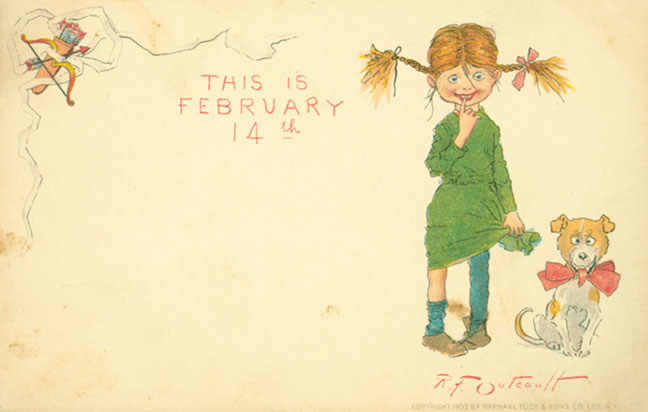 York World, the New York Journal, Judge, and the New York Herald. It was during this time that he created his first famous character of his “Hogan’s Alley” cartoon, the Yellow Kid. By 1902, R.F. introduced his famous Buster Brown and his faithful terrier, Tige. And, his personal style of using panels and dialogue balloons became a standard in cartooning.
York World, the New York Journal, Judge, and the New York Herald. It was during this time that he created his first famous character of his “Hogan’s Alley” cartoon, the Yellow Kid. By 1902, R.F. introduced his famous Buster Brown and his faithful terrier, Tige. And, his personal style of using panels and dialogue balloons became a standard in cartooning.
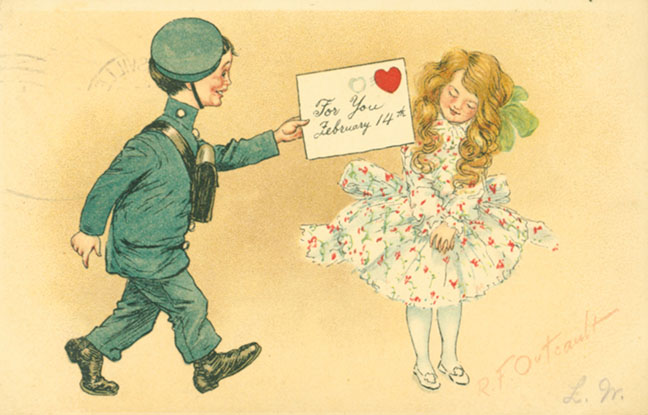 But those strange Valentine cards? They are unlike the sweet and lovey-dovey kids’ valentines of the late 20th century. Instead, there is an edge to Outcault’s art, a bit of an insult here and there, and more rejection than true love. In a way, they are an outgrowth of the so-called “Vinegar Valentines” of Victorian America. Vinegar valentines
But those strange Valentine cards? They are unlike the sweet and lovey-dovey kids’ valentines of the late 20th century. Instead, there is an edge to Outcault’s art, a bit of an insult here and there, and more rejection than true love. In a way, they are an outgrowth of the so-called “Vinegar Valentines” of Victorian America. Vinegar valentines 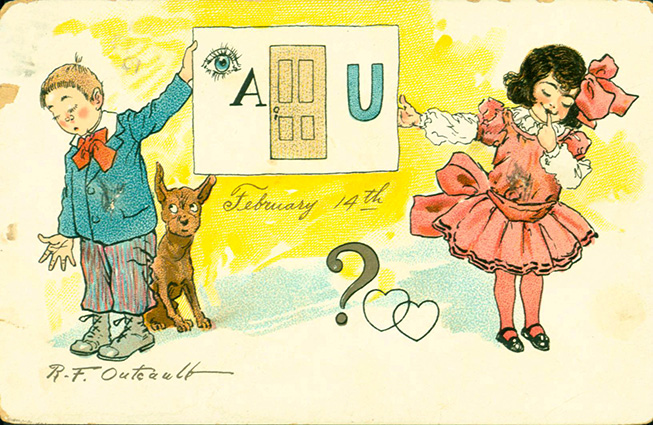 were sarcastic and insulting, greetings designed to reject the offers of true love. Competing with true romantic valentines, these little missives of misanthropy usually were sent anonymously to those one disliked, be they flirtatious bachelors or suffragists. Outcault’s cards resemble them in a natural progression, one supposes, from invective to just strange little takes on the whole idea of Valentine’s Day.
were sarcastic and insulting, greetings designed to reject the offers of true love. Competing with true romantic valentines, these little missives of misanthropy usually were sent anonymously to those one disliked, be they flirtatious bachelors or suffragists. Outcault’s cards resemble them in a natural progression, one supposes, from invective to just strange little takes on the whole idea of Valentine’s Day.
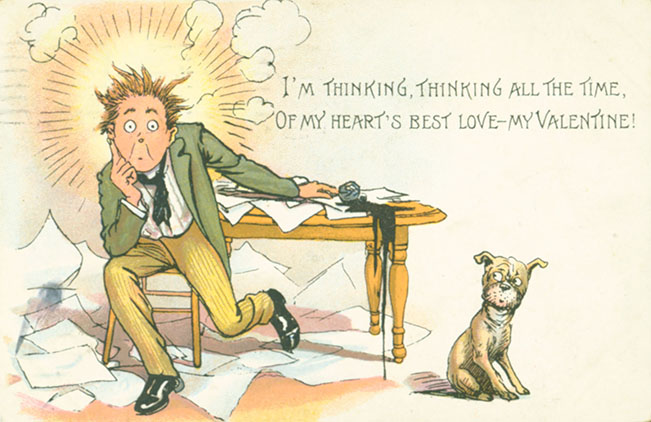 For R.F. Outcault, his valentine postcards were done in his typical style and represent another aspect of what was a long and productive cartooning career. Retiring from the hubbub of daily newspaper work, he spent the last decade of his life quietly painting and died in 1928.
For R.F. Outcault, his valentine postcards were done in his typical style and represent another aspect of what was a long and productive cartooning career. Retiring from the hubbub of daily newspaper work, he spent the last decade of his life quietly painting and died in 1928.
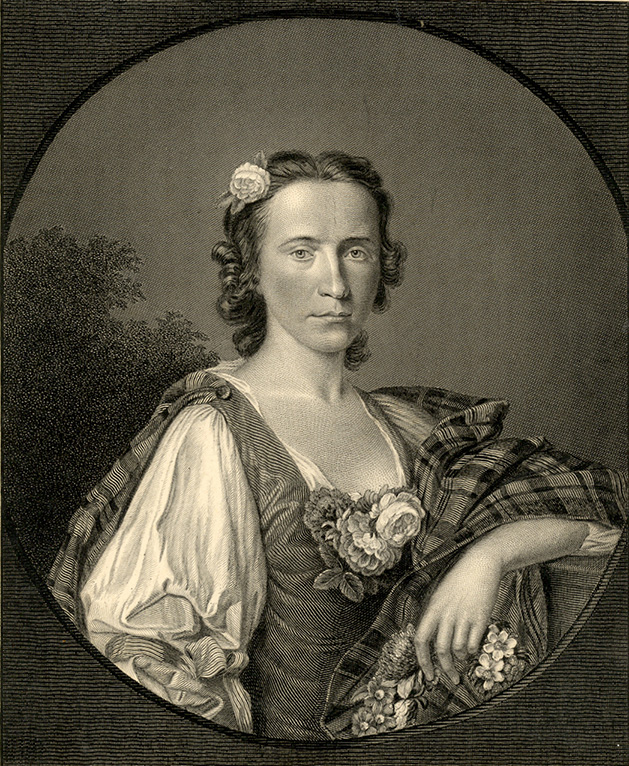 In every piece of history, there is a powerful woman, sometimes hidden or obscured from the record, that made all of the difference. This is true of the Jacobite movement as well, and though there are many incredible women that contributed to the movement, today’s post will focus on an incredibly special one. Flora Macdonald, with her bravery and commitment, saved a man’s life. What is even more incredible is that she not only saved a man’s life, but one that is integral to Scottish history.
In every piece of history, there is a powerful woman, sometimes hidden or obscured from the record, that made all of the difference. This is true of the Jacobite movement as well, and though there are many incredible women that contributed to the movement, today’s post will focus on an incredibly special one. Flora Macdonald, with her bravery and commitment, saved a man’s life. What is even more incredible is that she not only saved a man’s life, but one that is integral to Scottish history.


 Read Source, the online newsletter, to learn more about the news, events, people and happenings in UC Libraries.
Read Source, the online newsletter, to learn more about the news, events, people and happenings in UC Libraries.