The UC Health Sciences Library (HSL) has partnered with Read QxMD to bring you easy access to the HSL’s journal subscriptions.
Get set up quickly and easily.
- Download Read by QxMD by going to http://qx.md/read or search in the app store.
A web version is also available at https://readbyqxmd.com
- Add University of Cincinnati to your “Account Settings” under “Institutional Access”.
Already have Read by QxMD?
Add University of Cincinnati to your “Account Settings” under “Institutional Access” to gain continuous access to UC HSL’s journal subscriptions.
Get to know Read by QxMD
- Provides a single place to keep up with new medical and scientific research
- Filter for your professional specialty/location and favorite journals
- Save collections of articles important to you
- Auto-login when off-site



 Read Source, the online newsletter, to learn more about the news, events, people and happenings in UC Libraries.
Read Source, the online newsletter, to learn more about the news, events, people and happenings in UC Libraries. UC Libraries will be closed Monday, September 2 for Labor Day, except for the
UC Libraries will be closed Monday, September 2 for Labor Day, except for the 
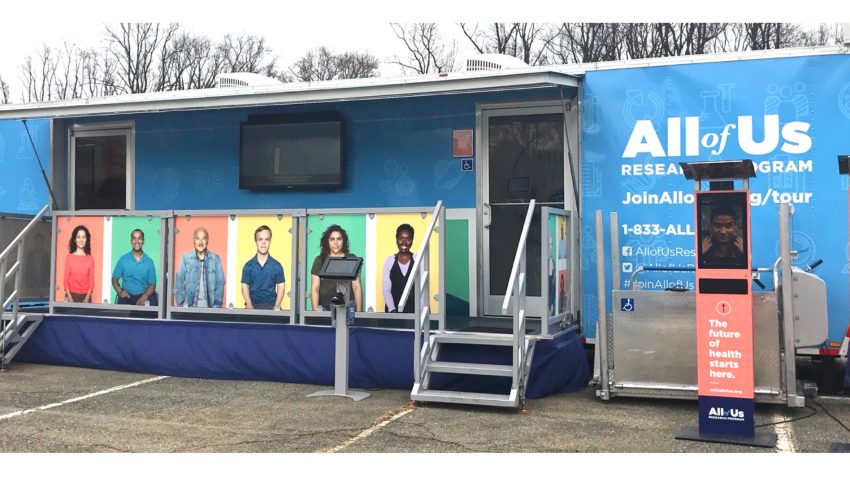

 The Donald C. Harrison Health Sciences Library will host the All of Us awareness and education mobile unit on Friday, June 21 from 10:00 a.m. – 4:30 p.m., 231 Albert Sabin Way, Kresge Circle.
The Donald C. Harrison Health Sciences Library will host the All of Us awareness and education mobile unit on Friday, June 21 from 10:00 a.m. – 4:30 p.m., 231 Albert Sabin Way, Kresge Circle.